Besides breast reduction, breast augmentation or tummy tuck, calf reduction plays a minor role in plastic surgery.
Nevertheless, those (mostly women) who can’t cope with their large calves suffer from psychological stress like women who wish to have their breast augmented or reduced.
At this point we’d like to inform you about the possibilities of calf reduction. We will inform you about surgical and non-surgical methods, explain the details and inform about risks and side-effects.
At last, you will be able to make a decision whether you want a change and how it will be performed. It’s all up to you and your individual well-being.
On this website Dr. Rene Schumann (Board certified Plastic Surgeon from Germany) shows you how to reduce calves.
At first, it is necessary to examine whether your large calves are based on fat deposites or muscular hypertrophy. Sometimes both aspects have to be considered at the same time.
Content
Yuveo Klinik
Characteristics of calf reduction
Our plastic surgeons at the Yuveo Clinic Düsseldorf decide which surgical procedures to use to reduce the calves, depending on the cause.
Rather rare surgery
Too much fat
Too much muscle
Abstaining from training
Calf reduction - muscle surgery
If the excessively strong calf muscles (calf hypertrophy) are the cause of the increase in circumference, a significant reduction in calf size can only be achieved by removing part of the calf muscles.
Those patients who want calf surgery have suffered from psychological strains for a long time. Wearing shorts or skirts which show the calves is avoided. Swimming or relaxing at the beach do not belong to their order of day. Some of them have even struggle to find proper boots which fit them.
Removing the muscle
Removing the muscle is highly effective. For this surgery we recommend a spinal or general anaesthesia.
Depending on skin quality: we make an approximately 5 cm transverse incision in the hollow of the knee. Furthermore, there is a 5 cm longitudinal incision halfway down the lower leg.
These incisions are sufficient for removing the gastrocnemius muscle. Our surgeons do not affect any large nerves or vascular structures which you can find in deeper layers of the tissue.
After the muscle is removed, we insert a drainage, if needed, then the wound is closed.
Result:
Removing the calf muscle in this way offers you a reduction of about 5 to 7 cm.
Benefit:
This surgery method is highly efficient because the hypertrophied muscle is removed.
Impediment:
- Scars
- Greater loss of strength in the short term
- We remove healthy tissue.
- Especially in calves with very little fatty tissue, the inner contour in the upper part of the calf looks somewhat unnatural.
Removing a part of the muscle
However, partial removal of the described muscles is also possible. For example, only the inner muscle belly of the gastrocnemius muscle can be removed.
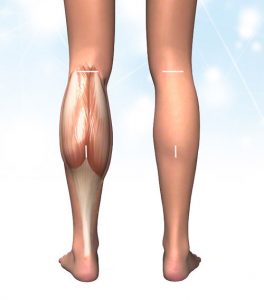
The picture shows calf hypertrophy with the gastrocnemius muscle on the left. On the right: reduced calf. The white lines show the incision required for calf reduction and the resulting scar length.
Frequently asked questions: Calf reduction
What are the indications for calf reduction?
The choice of calf reduction technique depends on what caused the calf to become too robust.
Often bulky calves (also known as “radish calves” or “radish legs”) are caused by simple accumulation of fatty tissue; in this case, liposuction is the best method for calf reduction.
In many cases, however, the calf muscle is also excessively thick. Liposuction has no effect in these cases. Extreme growth of the calf area can be observed in patients with muscular dystrophy. Muscular dystrophy is a hereditary disease which takes many different forms. Aesthetic concerns are not the main issue for patients with muscular dystrophy, making surgical calf reduction pointless.
Internal factors that create ‘fat calves’, such as water retention (edema) or lymphostasis (lymphedema), also require treatment for the cause of the problem, not cosmetic surgery.
What about selective neurectomy?
A selective neurectomy (denervation, nerve transection) is the separation of the nerve trunk which innervates the gastrocnemius muscle.
If your calf consists mainly of fat then a calf liposuction will be the solution. After the neurectomy, the muscle atrophies, reducing the muscle’s volume.
This procedure is a partial muscle reduction.
How is the endoscopic partial removal of the muscle performed?
Endoscopic calf reduction is well-known in Asia (Korea).
Depending on modeling one or both muscle heads surgeons make one or two 2 cm incisions in the hollow of the knee. This means that only part of the gastrocnemius muscle is removed. Surgeons make use of a special salpel which cuts using electricity and heat. This allows to maintain the natural shape of the calf.
Benefits:
- Only small incisions
- Calves are individually shaped.
- Loss of strength is minimized.
Impediments:
- We remove healthy muscle tissue.
- The effect is smaller than with complete muscle removal.
- Irregular contours can occur if the surgery lacks of a smoothly shaped surgery area.
- If the surgeon is unable to shape the area cut out of the muscle smoothly then there could be visible Postoperative care:
We have mentioned the general postoperative care already. In addition, we recommend that you perform intensive stretches multiple times a day for several months. It prevents shrinking of the scar.
Is calf surgery with liposuction possible?
Calf reduction by liposuction is a good treatment option if the increase in circumference is caused by an accumulation of fatty tissue.
The amount of excess fatty tissue can also be tested by any non-medical person by squeezing the tissue with two fingers. If there is almost only skin here, the calf consists mainly of muscle. Calf reduction with liposuction is then not promising.
Calf correction with liposuction rarely results in unevenness. Restraint is used on the ankles because swelling and pigment changes can occur with a radical procedure.
The recovery phase depends on the amount of suction. It can last a few days, but also a few weeks (in the case of extreme findings). In principle, sports should be avoided for 6 weeks and support stockings should be worn for the same length of time.
Advantages:
Calf reduction by liposuction results in only a few small barely visible scars (puncture marks).
Disadvantages:
If the calves have a large amount of muscle and a small amount of fat, only a small reduction in circumference can be expected.
Is Btx treatment appropriate?
We should also mention the Btx® calf reduction method (8). Btx is a neurotoxin which causes myoparesis (slight muscular paralysis). Botulinum toxin is currently a standard treatment for mimetic wrinkles. It also has other uses, however – including calf reduction.
Is radio frequency useful to reduce the calves?
Radio frequency calf reduction refers to obliteration of the muscle through several small skin punctures using electricity and heat.
The procedure can be performed to varying degrees of intensity, but usually requires general anesthetic.
Is abstaining from exercise an option for reducing the calf?
Calf reduction can be achieved by abstaining from exercise. If the calves are perceived as too large due to intense physical activity, the enlargement can be reduced by avoiding certain exercises and types of training.
Exercises which build up calf muscle should be avoided, in particular standing on your toes with and without weights, climbing stairs, hiking, and sprinting.
How is post-operative care performed?
For three months: Bandaged legs or surgical stockings.
Thrombosis prophylaxis may be necessary. It depends on the immobilization.
Our surgeons recommend inpatient care for 24 h after calf surgery.
Walking safely with crutches (the first two or three days)
During the first two weeks after surgery we recommend physical reserve and elevation of the legs.
Abstain from sport for approx.. six weeks.
Full function: after a few weeks
Regaining muscle strength: You have to calculate up to six month.
6 months for the calf muscles to regain their full strength
Checking the facts
- Surgeons: Dr. Schumann and Dr. Schumann-Averkiou
Anesthesia:
General anesthesia- Hospital:
Inpatient for one day - Postoperative care:
Heparin, compression, crutches - Sport:
Abstain from sport for six weeks
Further information
More about calf reduction surgery.
Other studies, mostly from Asia, have shown benefits in calf reduction by neurectomy (separating the gastrocnemius muscle’s nerve branch) and removing the muscle tissue with radio frequency.
Btx. can be used to paralyzed the calf muscle. The Btx is injected into the muscle without anaesthesia via many small punctures (10 -15 per side).

