The actual calf muscle, located on the achilles tendon, is the triceps surae muscle (three headed calf muscle). This muscle is made up of the soleus muscle and the two headed gastrocnemius muscle. The former is essential for the function of the calf. The latter is an accessory muscle, whose loss does not lead to any change in function.
The function of the muscle is simply assumed by other muscles (1,2). This is why the gastrocnemius muscle is frequently used in plastic surgery as a muscle flap to fix defects in the knee region.
Content
Yuveo Klinik
Characteristics of calf muscles
The main calf muscles in the lower leg are the:
Gastrocnemius muscle and soleus muscle.
General information about calf muscles
The calf (sural region) is the rear upper muscular region of the lower leg.
Not all muscles in the calf are calf muscles, however. The calf is defined largely as the three headed calf muscle (triceps surae muscle).
In anatomy, we actually talk about the lower leg muscles and divide them into the following categories:
- Deep Layer
- Superficial Layer
- Anterior Compartment
- Posterior Compartment
- Lateral Compartment
You can find more details under the headings superficial lower leg muscles and deep lower leg muscles.
There are, however, only two muscles called calf muscles:
- two headed calf muscle = Gastrocnemius muscle
- soleus muscle
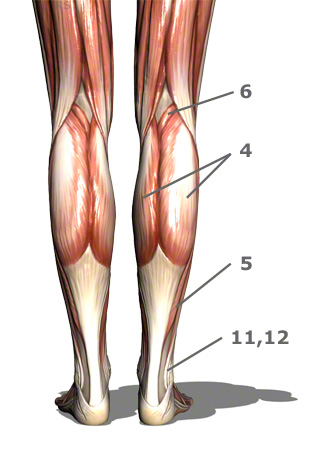
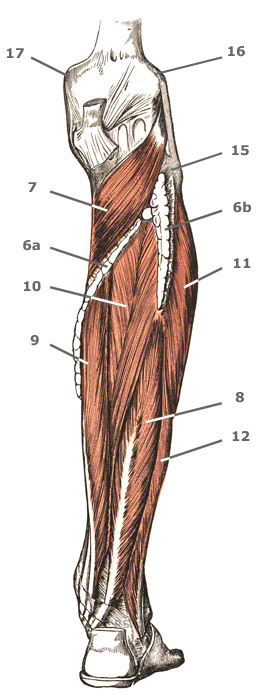
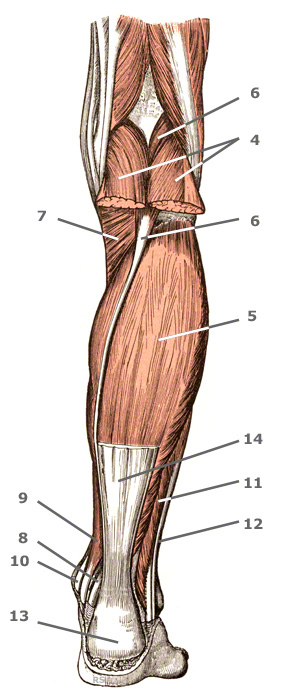
The muscles in detail
4+5. The triceps surae muscle is a three-headed calf muscle.
The two headed calf muscle combined with the soleus muscle is regarded as the triceps surae muscle, thus forming one of the strongest human muscles.
The plantaris muscle can be considered the fourth, vestigial head of the calf muscle.
4. The gastrocnemius muscle is also designated two-headed calf muscle or twin calf muscle.
The two headed calf muscle belongs to the rear group of the superficial layer. It is the lower leg muscle which definitively shapes the outside of the calf. It’s two heads can be easily seen when you stand on your toes.
- Function: powerfully flexes the foot and can turn it outwards
- Origin: lateral head: thigh bone away from the body and the lateral condyle – medial head: medial condyle of the thigh bone.
- Base: from the soleus muscle tendon as the achilles tendon on the heel bone (calcaneus)
- Innervation: Muscle branch of the deep fibular nerve
This calf muscle has two different uses for Plastic Surgery.
On the one hand, it can be used to correct defects in the knee area. On the other hand it can be removed or partially removed for a Calf Reduction if the calf is too large (hypertrophy of the calf muscles) without any loss of function.
If the calf is very small (hypotrophy of the calf muscles) then the patient could decide on a Calf Augmentation using Calf Implants. The calf implants are usually placed between the gastrocnemius muscle and the fascia of the lower leg.
You can find more general information in the section Calf surgery.
5. Soleus Muscle
Defects (which occur after injuries or tumorresection) to the middle of the lower leg can be covered by the soleus muscle, which provides a reliable muscle flap for use in reconstructive surgery.
- Function: powerfully flexes the foot and can turn it outwards
- Origin: Head and upper 1/3 of the fibular (5b), rear surface of the shin (5a)
- Base: with the gastrocnemius over the achilles tendon on the heel bone
- Innervation: Branch of the tibialis nerve
6. The German name for the plantaris muscle is the "long calf muscle."
This calf muscle is very long if you include the tendon in the measurement, but also very slight and therefore practically without function.
- Origin: Thigh bone around the hollow of the knee
- Base: Achilles tendon
- Innervation: Branch of the tibialis nerve
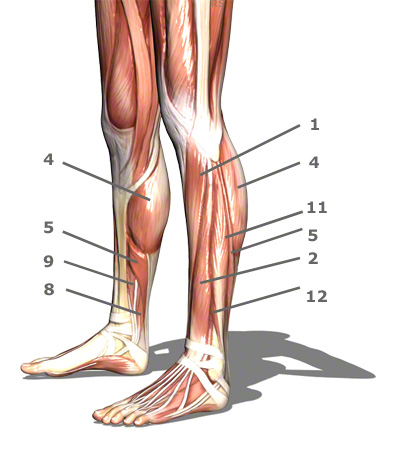
Further information
Legend:
1. Tibialis anterior muscle (front shin muscle)
2. Extensor digitorum longus muscle (lateral toe pointer)
3. Extensor hallucis longus (lateral big toe pointer)
4. Gastrocnemius muscle – two headed calf muscle
5. Soleus muscle
6. Plantaris muscle – lateral calf muscle
7. Popliteus muscle – muscle of the knee’s hollow
8. Flexor hallucis longus muscle (lateral muscle that bends the big toe)
9. Flexor digitorum longus muscle (lateral muscle that bends the toes)
10. Tibilias posterior muscle (rear shin muscle)
11. Fibularis longus muscle (peroneus longus muscle) (lateral fibula muscle)
12. Fibularis brevis muscle (peroneus brevis muscle) (short fibula muscle)
13. Heel bone (Calcaneus)
14. Achilles tendon
15. Head of the fibula
16. Outer condyle of the thigh bone
17. Inner condyle
Further topics: