Oversized ears can be corrected by means of ear reduction (or auricle reduction).
The medical technical term for a developmentally large ear is macrotia. The definition is not fixed; the relative size depends on body and head size.
The approximate normal value for the ear axis length for women lies between 58 and 62 mm and for men between 62 and 66 mm.
In general, the psychological distress of the affected person, often strengthened by wisecracks and teasing, is critical for the indication for ear reduction.
Content
Yuveo Klinik
Characteristics of ear reduction
Low-scar procedures are used at Yuveo in Düsseldorf to bring ears back “into shape”.
Ear reduction
Reducing the macrotia
Earlobe correction
Ear reduction surgery
What is the procedure for ear reduction surgery?
Ear reduction can be carried out on an ambulatory basis under local anesthesia, possibly with the addition of twilight sleep. General anesthesia is advisable for anxious adults and for children. The hair and ears must be thoroughly cleaned before the intervention.
After the ear reduction, a large compressive cotton dressing is applied for only 2-3 days.
After that a smaller dressing with a loose fitting headband usually suffices.
How is ear reduction for macrotia performed?
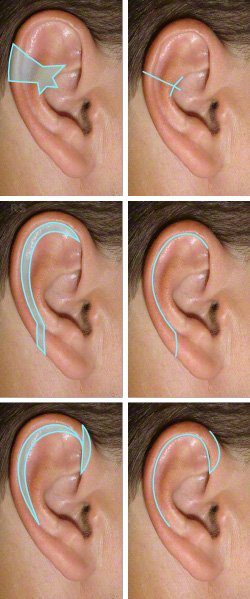
In 1856, Di Martino had already described a method for ear reduction for the first time. It concerned a wedge resection technique, similar to that shown in pictures 1 and 2 above. Many further descriptions followed.
Today various techniques are utilized, associated with well hidden, inconspicuous scars (the scar lines can be seen in the pictures).
Planning for the surgery first includes a thorough examination of the ears.
The choice of surgical technique depends on the areas that require revision. Also, it can make sense to combine the ear reduction with ear pinning and/or ear lobe correction surgery.
The principle consists of removing excess skin and cartilage to ultimately form a natural looking ear.
Accurate suturing technique is of vital importance to an outcome with inconspicuous scars and an auricle with no step-offs.
Not to be underestimated, however, is the appropriate involvement of the patient to prevent tractive forces on the fine sutures.
FAQ: Ear reduction
What does the postoperative care involve?
- Dressing – After ear reduction surgery the ears are molded with cotton wadding, for example, and then enclosed under a rather large ear dressing. This stays in place for 1-7 days.
- Headband – Following the ear reduction, a headband should be worn for about 2 weeks, 24 hours per day. After that, it is sufficient to wear it overnight for another 2-3 weeks. As opposed to its use in ear pinning, the headband in the case of ear reduction surgery does not need to be tight, but is merely thought of as protection.
- Stitches can be removed after about 2 weeks.
- Sport – So as not to negatively affect the outcome of an ear reduction, team and ball sports are to be avoided for 6-12 weeks.
What complications can occur during ear reduction surgery?
A surgical adage maintains that there are only 2 types of surgeons who have no complications:
Those of the first type do not operate, and those of the second are liars.
As plastic surgeons we explain complications and warning signs to you in detail,
so that they can be detected in a timely manner and treated adequately to avoid worsening.
In the following, the most important complications that can occur with an ear reduction are briefly described:
- Swelling
Massive swelling of the ear can develop after ear reduction. To minimize this, measures to reduce swelling are helpful: cooling, elevation of the upper body during sleep and appropriate medications. - Hematomas
The above described swelling after ear reduction sometimes leads to bruising of the skin. A true hematoma, which lies in the subcutaneous tissue, is the exception, especially if a well-fitting pressure dressing is applied postoperatively. - Bleeding
This is avoided by use of careful hemostasis and compression. Aside from that, the wound surface is small, which lessens the chance of occurrence. - Disturbance of feeling in the skin after ear reduction
Impairment of skin sensation can occur. However, this is usually reversible. - Disturbance of scar formation
So called hypertrophic scars (or, in the worse cases, keloids) are rare in the ear region. These can be treated, if they occur, with special salves and, where appropriate, cortisone injections, among others, more or less successfully. If a disturbance of scar tissue is known, depending on severity, it must be seriously considered whether an ear reduction should be performed at all. - Infections
Infections are decidedly rare after an ear reduction. If infections are not treated in a timely manner, they can spread to the ear cartilage (chondritis). - Tearing of the wound / sutures.
With an ear reduction, careful attention must be given to protect the suture line. Even a small impact can rip the fine sutures out. Incidentally, this also applies to the invisible cartilage sutures. Therefore it is safer to wear a headband for a few weeks for protection. - Unsatisfactory cosmetic results
Before ear reduction surgery, the patient’s desires must be understood by the surgeon and the feasibility assessed. If dissatisfaction persists for operative reasons or because complications occurred, then generally a repeat ear revision is performed. - The risks of narcotics / anesthesia will not be addressed here.
Checking the facts
- Surgeons: Dr. Schumann and Dr. Schumann-Averkiou
- Anaesthesia: local anaesthesia, maybe with twilight sleep
- Hospital: ambulantory basis
- Postoperative care: ear dressing for one to seven days, headband
- Sports: No sports for six to twelve weeks after surgery
Further information
Otoplasty:
The most commonly performed form of otoplasty is ear pinning. The ear reduction described on this page is a rather uncommon surgery.
